What is Domain Name?
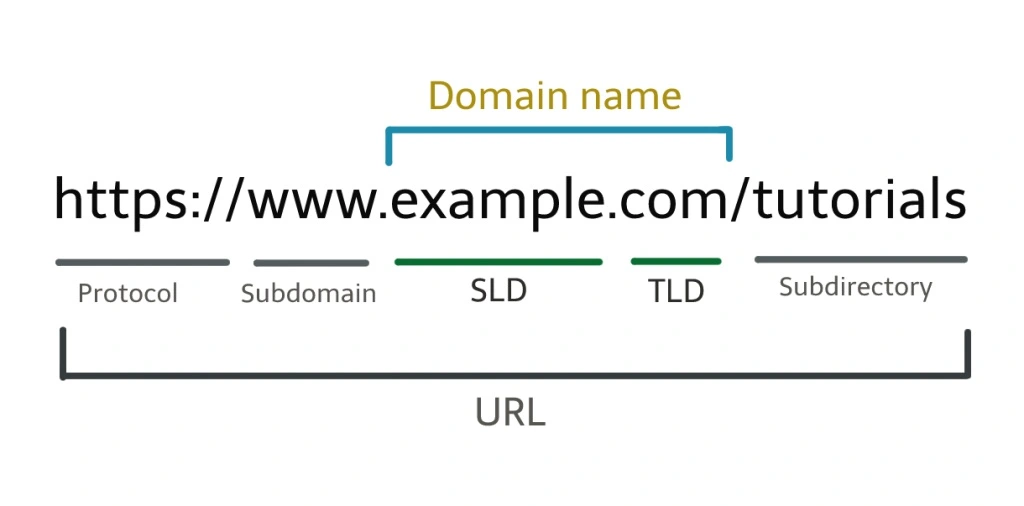
A domain name is a unique and human-readable identifier that represents a specific location on the internet. It’s part of a website’s URL (Uniform Resource Locator) and is used to access web pages, online services, and resources. Domains are organized hierarchically and typically consist of two main parts
Table of Contents
Domain names consist of two main parts:

- Domain Name: This is the main part of the domain that you type into a web browser to visit a website, such as “example.com” or “google.com”. It can include letters, numbers, and hyphens, but no spaces.
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): This is the extension at the end of a domain name, such as “.com”, “.org”, “.net”, “.edu”, “.gov”, “.co.uk”, etc. TLDs serve different purposes and can indicate the type of organization or geographical location associated with the domain.
Domains play a crucial role in navigating the internet because they provide a more user-friendly way to access websites and online resources compared to using IP addresses (e.g., 192.168.1.1). Additionally, domains can be used for email addresses, making them an essential part of online communication and branding.
Why we need domain.

We need domains for several important reasons:
- Easy Access: Domains provide a user-friendly way to access websites and online services. Instead of remembering complex IP addresses, users can simply type a dn into their web browser to visit a specific website.
- Brand Identity: Domains play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining a brand identity on the internet. A unique and memorable dn can help differentiate your business or organization from others and make it easier for customers to find you online.
- Professionalism: Having your own dn (e.g., yourbusiness.com) adds a level of professionalism to your online presence. It conveys trust and credibility to visitors, especially if you’re running a business or providing services online.
- Email Addresses: Domains are also used for creating custom email addresses (e.g., info@yourbusiness.com). This not only looks professional but also reinforces your brand identity in communication with clients, customers, and stakeholders.
- Control and Ownership: Owning a domain gives you control over your online presence. You can choose where your domain points (e.g., to a website, email server, or other online services) and manage its settings, such as DNS configurations and security measures.
- Marketing and SEO: A well-chosen dn can contribute to your marketing efforts and search engine optimization (SEO) strategy. It can include keywords relevant to your business or industry, making it easier for potential customers to find you through search engines.
Overall, domains are essential for establishing a professional online presence, building brand recognition, facilitating communication, and enhancing your visibility and accessibility on the internet.
How To Register a Domain Name

To register a domain name, follow these steps:
- Choose a Domain Name: Decide on the domain name you want for your website. It should be unique, easy to remember, and relevant to your brand or purpose.
- Check Availability: Use a domain registrar’s website to check if your desired domain name is available. If it’s already taken, you may need to come up with variations or choose a different name.
- Select a Registrar: Choose a domain provider to register your domain name. Compare prices, features, and customer support before making a decision.
- Register the Domain: Once you’ve selected a registrar, proceed to their website and enter the domain name you want to register. Follow the prompts to complete the registration process.
- Provide Contact Information: During registration, you’ll need to provide your contact information, including your name, address, email address, and phone number. This information is used for administrative purposes and to contact you regarding the domain.
- Choose Registration Period: Select the registration period for your domain name. You can usually register a domain for one year or longer, depending on your needs and budget.
- Add Domain Privacy (Optional): Consider adding domain privacy protection to hide your personal contact information from the public WHOIS database. This helps prevent spam and unwanted solicitations.
- Complete the Payment: Provide payment information to complete the registration process. Make sure to review the total cost, including any additional services you’ve selected.
- Verify Registration: After payment, you’ll receive a confirmation email from the registrar with details about your domain registration. Verify the information to ensure everything is correct.
- Manage Your Domain: Use the registrar’s online dashboard to manage your domain settings, such as DNS configurations, domain forwarding, and renewal options.
That’s it! Once your domain name is registered, you can start using it for your website, email, and other online services.
