What Is Port 443?

Port 443 is a well-known port number in the context of computer networking and the Internet. It is associated with the HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) communication protocol, which is used to secure the transfer of data between a user’s web browser and a website.
When you visit a website that uses HTTPS, the communication between your browser and the website’s server is encrypted to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the data being transmitted. This is particularly important when sensitive information such as login credentials, personal details, or financial data is involved.
Port 443 is the default port for HTTPS traffic, and it is widely used for secure web browsing. When you type “https://” in the address bar of your web browser, it implies that the communication will take place over port 443. The use of encryption helps protect against eavesdropping and other forms of cyber threats.
Table of Contents
How Does HTTPS Work?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a protocol that provides a secure communication channel over a computer network, commonly the Internet. It ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the data exchanged between a user’s web browser and a website’s server. Here’s an overview of how HTTPS works:
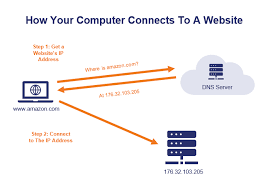
- Handshake Process:
- Client Hello: The process begins when a user’s web browser initiates a connection to a website by sending a “Client Hello” message. This message includes information about supported cryptographic algorithms and other parameters.
- Server Hello: The website’s server responds with a “Server Hello” message, indicating the chosen cryptographic parameters for the communication session.
- SSL/TLS Encryption:
- Key Exchange: The client and server negotiate and agree upon a set of cryptographic keys to be used for securing the communication. This is typically done using a process called the key exchange, and it can involve asymmetric (public-key) cryptography.
- Symmetric Encryption: Once the keys are exchanged, the actual data transfer is encrypted using symmetric encryption. This means that both the client and server use the same shared key to encrypt and decrypt the data.
- Secure Data Transfer:
- With the encryption keys established, all data exchanged between the client and server is encrypted before transmission and decrypted upon receipt. This ensures that even if intercepted, the data is unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
- Digital Certificates:
- The server typically presents a digital certificate during the handshake process. This certificate is issued by a trusted third party known as a Certificate Authority (CA). The certificate contains the server’s public key and information about the website. The client uses this information to verify the authenticity of the server.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS):
- HTTPS can use either SSL or TLS protocols to establish a secure connection. While SSL was the original protocol, it has been largely replaced by the more secure and modern TLS. The terms “SSL” and “TLS” are often used interchangeably in common language, but it’s essential to note that TLS is the more up-to-date and secure version.
By employing these mechanisms, HTTPS ensures that the data transmitted between a user and a website is encrypted and secure, reducing the risk of eavesdropping, data tampering, and other security threats. This is especially important for protecting sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal details, and financial data, during online transactions and interactions.
What Does HTTPS Port 443 Protect and Why Do We Need It?
HTTPS, specifically using port 443, protects the data exchanged between a user’s web browser and a website’s server during communication over the Internet. The primary purposes of HTTPS and port 443 are to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the information being transmitted. Here’s why HTTPS on port 443 is crucial:

- Confidentiality:
- Encryption: HTTPS uses encryption to scramble the data exchanged between the client and server. This means that even if a malicious actor intercepts the communication, they would see only encrypted data, making it extremely difficult to decipher without the encryption key. This is particularly important for protecting sensitive information such as login credentials, personal details, and financial transactions.
- Integrity:
- Data Integrity Checks: HTTPS employs cryptographic mechanisms to ensure the integrity of the data. This means that any attempt to tamper with or modify the data during transit would be detected. If the data is altered, the recipient will notice that it does not match the expected integrity checks, and the communication may be aborted.
- Authentication:
- Digital Certificates: HTTPS uses digital certificates to establish the authenticity of the website’s server. These certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs), and they contain information about the server’s public key and the identity of the website. This helps users verify that they are connecting to the legitimate website and not a malicious imposter.
- Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:
- Securing Against Eavesdropping: Without HTTPS, data sent over the Internet is transmitted in plain text, making it susceptible to eavesdropping. Malicious actors could intercept and read sensitive information, such as login credentials or personal messages. HTTPS prevents this by encrypting the data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Building User Trust:
- Visual Indicators: Browsers typically display visual indicators, such as a padlock icon or the word “Secure,” to indicate that a website is using HTTPS. This helps build trust among users by signaling that their connection is secure and that the website takes measures to protect their data.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
- Legal and Industry Standards: Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards require the use of HTTPS for handling sensitive information. Adhering to these standards is essential for compliance and helps organizations meet legal requirements regarding data protection.
Summary

In summary, HTTPS on port 443 is essential for securing the transmission of sensitive information over the Internet. It protects against eavesdropping, data tampering, and man-in-the-middle attacks, while also providing users with visual indicators of a secure connection. The encryption, integrity checks, and authentication mechanisms of HTTPS contribute to a safer online environment, making it a fundamental component of secure web communication.
