SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and it is a standard protocol for securing communication over a computer network.

SSL is commonly used to secure data transfer between a user’s web browser and a website, but it can also be used to secure other types of data transfer, such as email, file transfer, and voice over IP.
The SSL protocol works by establishing a secure connection between a client (such as a web browser) and a server (such as a website).
Table of Contents
What is SSL Security?
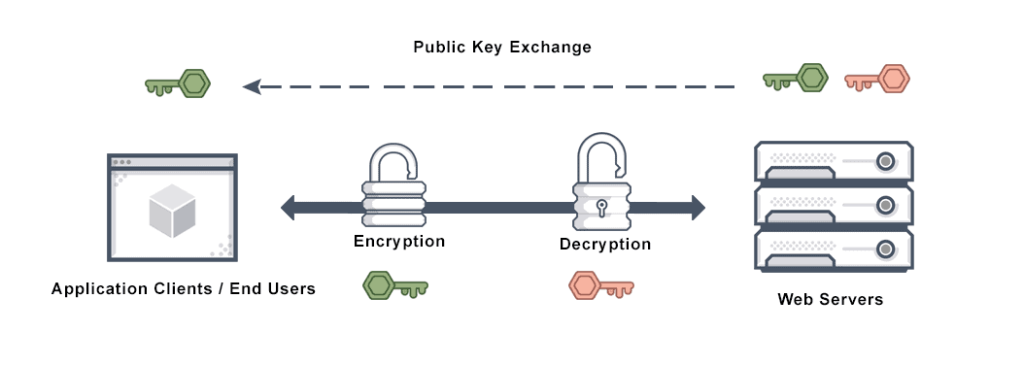
It is a security protocol that determines how to encrypt data using specific algorithms. The secure socket layer SSL protocol assesses both the data to transmit and the link and determines encryption variables for both.
SSL security technology establishes encrypted links between clients and servers. For example, it scrambles sensitive information transferred between a client, often a website, and a user, often a browser or mail server.
Difference between SSL And HTTPS
There is a bit of confusion in your question, as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are not directly comparable.
SSL vs. HTTPS
SSL: It is a protocol used for securing communication over a computer network. It provides a secure connection by encrypting the data exchanged between a client (such as a web browser) and a server. However, It has been largely deprecated due to security vulnerabilities, and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), is now the recommended protocol.
HTTPS: HTTPS, on the other hand, is not a protocol but rather an extension of HTTP. It stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure and indicates that the communication between the user’s browser and the website is secured using either SSL or TLS. So, when you see “https://” in a URL, it means that the website is using a secure protocol (either SSL or TLS).
FOR MORE INFORMATION: https://www.trichywebhosting.com/
Which type of SSL certificate do I need for my website?

The right SSL certificate for your website depends on various factors, including the type of website, the level of trust you want to establish, and the specific security features you require. Here are some common types of SSL certificates:
Domain Validation (DV) Certificates
- Purpose: Suitable for basic encryption and securing the connection.
- Validation Process: Only domain ownership is verified.
- Use Case: Personal websites, blogs, small business sites where encryption is the primary concern.
Organization Validation (OV) Certificates
- Purpose: Provides a higher level of trust by verifying the organization’s details.
- Validation Process: Verifies domain ownership and organization details.
- Use Case: Business websites, e-commerce sites, sites that want to show organizational legitimacy.
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates
- Purpose: Highest level of trust, prominently displays the organization’s name in the browser.
- Validation Process: Rigorous validation of domain ownership and extensive organization vetting.
- Use Case: E-commerce, financial, or other websites where users need high assurance of the site’s authenticity.
Wildcard Certificates
- Purpose: Secures a main domain and all its subdomains with a single certificate.
- Validation Process: Typically DV or OV validation for the main domain.
- Use Case: Websites with multiple subdomains, such as blog.example.com, shop.example.com.
Multi-Domain (SAN) Certificates
- Purpose: Allows securing multiple domains with a single certificate.
- Validation Process: DV, OV, or EV based on the certificate type and the domains involved.
- Use Case: Businesses with multiple domains or websites.
Single Domain Certificates
- Purpose: Secures a single domain.
- Validation Process: DV, OV, or EV based on the certificate type chosen.
- Use Case: Websites with a single domain.
What Causes SSL Security Errors?
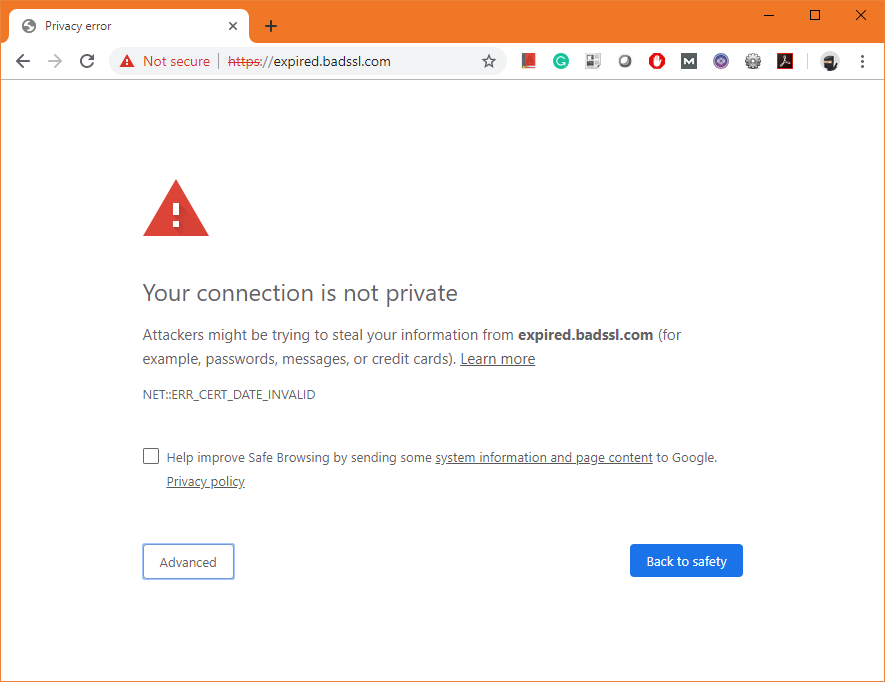
An SSL certificate error occurs when a web browser can’t verify the SSL certificate installed on a site. Rather than connect users to your website, the browser will display an error message, warning users that the site may be insecure.
What are the benefits of SSL?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security technology that establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a browser, ensuring that the data transmitted between them remains private and secure. SSL has been succeeded by TLS (Transport Layer Security), but the term “SSL” is still commonly used to refer to the security protocol. Here are some of the key benefits of using SSL/TLS:
- Data Encryption:
- One of the primary benefits of SSL is data encryption. When SSL is implemented, the information exchanged between the user’s browser and the web server is encrypted, making it difficult for malicious actors to intercept and understand the data.
- Data Integrity:
- SSL provides data integrity by using cryptographic methods to ensure that the information sent between the server and the client is not altered during transmission. This helps prevent data tampering or corruption.
- Authentication:
- SSL certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs), and they verify the identity of the website or server. This authentication feature helps users trust that they are connecting to the intended and legitimate website rather than a fraudulent one.
- Trust and Credibility:
- Websites with SSL certificates display a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, indicating a secure connection. Additionally, the URL starts with “https://” instead of “http://,” signaling to users that the website employs encryption. This helps build trust among visitors and enhances the credibility of the website.
- Protection Against Phishing:
- SSL helps protect against phishing attacks by ensuring that the information entered on a website (such as login credentials, personal details, etc.) is transmitted securely. This reduces the risk of sensitive information falling into the wrong hands.
- Search Engine Ranking Boost:
- Search engines, such as Google, consider SSL/TLS as a ranking factor. Websites with SSL certificates may receive a slight boost in search engine rankings compared to non-secure websites. This is part of efforts to encourage a more secure online environment.
- Compliance with Regulations:
- Many data protection regulations and standards, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), require the use of encryption to protect user data. Implementing SSL helps websites comply with these regulations and avoid potential legal issues.
- Secure Online Transactions:
- For websites that handle online transactions, such as e-commerce sites, SSL is essential for securing sensitive information like credit card details. It ensures that customer data is encrypted and protected during the entire transaction process.
- Securing Login Credentials:
- SSL is crucial for securing login credentials on websites. Whether it’s a user logging into an email account, social media platform, or any other service, SSL helps protect the username and password during the authentication process.
