What is the 403 Forbidden Error?

The 403 Forbidden Error is an HTTP status code indicating that the server understands the request but refuses to authorize it. This error typically occurs when a user tries to access a resource or perform an action for which they do not have the necessary permissions.
Table of Contents
Here are some common reasons for encountering a 403 Forbidden Error:
- File Permissions: The server’s file or directory permissions do not allow the requested action. For example, if a directory is not readable by the web server user, a 403 error will be returned.
- IP Restrictions: Access may be restricted to certain IP addresses. If your IP address is not on the allowed list, you will receive a 403 error.
- Authorization Rules: The server’s configuration might restrict access to certain users or groups. This can be managed through
.htaccessfiles, web server configuration files, or application-level settings. - Directory Browsing: If directory browsing is disabled on the server, and there is no default file (like
index.htmlorindex.php) present, a 403 error can occur when trying to access a directory. - Blocked by Security Plugins: In some cases, security plugins or modules on the server (like mod_security) can block access based on certain criteria, resulting in a 403 error.
- Hotlink Protection: If a server is configured to prevent other sites from linking directly to its resources (like images), and you attempt to access those resources directly, you might get a 403 error.
How to Fix the 403 Forbidden Error
Fixing a 403 Forbidden Error involves identifying and addressing the underlying causes. Here are detailed steps to help you resolve the issue:
- Check File and Directory Permissions:
- Ensure the correct permissions are set for files and directories.
- Files: Typically
644(readable by everyone, writable by the owner) - Directories: Typically
755(readable and executable by everyone, writable by the owner)
- Files: Typically
- Use an FTP client, SSH, or your hosting control panel to adjust permissions if needed.
- Ensure the correct permissions are set for files and directories.
- Inspect the .htaccess File:
- Look for rules in your
.htaccessfile that might be causing the block, such asdeny from allor specific IP deny rules. - Temporarily rename the
.htaccessfile to see if the error resolves, which can help you determine if the file is the cause.
- Look for rules in your
- Check Web Server Configuration:
- Review your web server configuration files (e.g.,
httpd.conffor Apache,nginx.conffor Nginx) for access restrictions. - Ensure the
AllowOverridedirective (for Apache) allows.htaccessfiles if you are using them.
- Review your web server configuration files (e.g.,
- Ensure Directory Indexing:
- Make sure the directory you are trying to access has an index file (e.g.,
index.html,index.php). - To enable directory browsing, you can:
- For Apache, add
Options +Indexesin your.htaccessor server configuration. - For Nginx, include the
autoindex on;directive.
- For Apache, add
- Make sure the directory you are trying to access has an index file (e.g.,
- Review IP Restrictions:
- Check for any IP restrictions in your
.htaccessfile, firewall rules, or server configuration. - Ensure your IP address is whitelisted if there are restrictions in place.
- Check for any IP restrictions in your
- Check Security Plugins and Modules:
- Review security plugins or modules like mod_security for Apache to see if they are blocking the request.
- Adjust security settings or whitelist the necessary URLs/IPs as needed.
- Disable Hotlink Protection:
- If hotlink protection is enabled, make sure your site’s URLs are allowed.
- Adjust hotlink protection settings in your hosting control panel or
.htaccessfile.
- Contact Your Hosting Provider:
- If you have checked the above steps and still encounter the error, contact your web hosting provider for assistance. They may have additional server-level security measures or restrictions causing the error.
Example .htaccess Configuration
Here’s an example of a .htaccess configuration that might help resolve common issues:
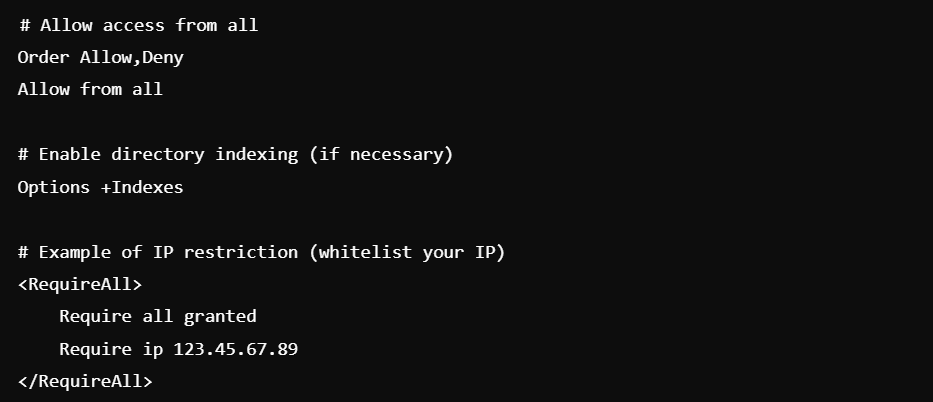
Detailed Steps for Common Platforms
For Apache:
Check Permissions:

Review .htaccess:
- Edit the
.htaccessfile and look for restrictive directives. - Temporarily rename the
.htaccessfile to see if the issue resolves.
Update Apache Configuration:
- Open
httpd.confor the relevant virtual host configuration file. - Ensure
AllowOverrideis set toAllif using.htaccess.
For Nginx:
Check Permissions:

Update Nginx Configuration:
- Open
nginx.confor the relevant server block configuration file. - Ensure there are no
denydirectives blocking access. - Enable autoindex if necessary:

By following these steps, you should be able to identify and resolve the cause of the 403 Forbidden Error.
